
Cartesian, Six-Axis, and SCARA robots all belong to the varied types of industrial robots. Manufacturing industries are turning towards the use of industrial robots in their production, and all three types of robots are highly involved. Each of them has been designed in a unique way that allows it to perform a particular task that the other probably cannot be able to do.
Production times are now faster as robots are able to work non-stop for hours without a need for taking even a single break. Add their speed and accuracy into the mix, and you are looking at a future where human labor in manufacturing plants will no longer be needed.
Table of Contents
What are Cartesian, Six-Axis, and SCARA Robots?

Source: Pinterest
At first glance, these robots may look the same to an untrained eye, but they go deeper than that. Most may have the same shape as each other but their design and the functions they handle are entirely different.
Before dissecting the things that set the three robots apart, it is important that we know what each of them is in the first place.
Cartesian Robots
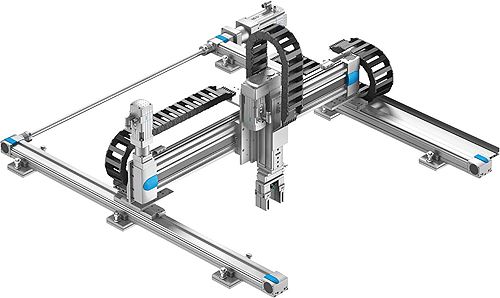
Source: Pinterest
Cartesian robots are sometimes called Gantry Robots, and they are the type that works from an overhead grid and uses linear actuators and motors to position tools. It has a rectangularly shaped work envelope whose size depends on the size of the grid. Cartesian robots have a three-dimensional movement; their rigidity makes them very precise when they are in operation. They are widely used as material handling robots and machine painting.
Six-Axis Robot

Source: Pinterest
A Six-Axis robot is the type that is mounted on a pedestal enabling its robotic arm to have more movement in all directions and the best control than the other two robots. As the name implies, a 6 axis robot has six axes that move in a three-dimensional manner on top of allowing it to position itself any way it wants. Their high flexibility makes them the ideal factory robotic arm for welding works, as a robotic palletizer, and as a machine tending robot.
SCARA Robot

A SCARA robot is among the best industrial robots. It has a circular work envelope and is mounted on a pedestal, making use of a four-axis robot arms move along a three-dimensional plane. At the end of the plane, they have something called a theta axis that gives them greater flexibility, a feature that makes them good palletizing robots, machine loading and unloading, and small part assembly robot.
The Differences Between Cartesian, Six-Axis, and SCARA Robots
So how exactly do Cartesian, Six-Axis, and SCARA robots differ from one another? To better distinguish them from one another, we will use the following parameters.
Load Capacity

Source: Pinterest
The maximum payload for each robot varies depending on the size of the robot and the task it has been designed for. As a rule for most robotic arms, a robot’s load capacity must exceed the total weight of the payload. Based on this, Cartesian robots are better placed to deal with heavier payloads compared to the other two. For SCARA and Six-Axis robots, they are limited because they support loads on their extended robotic arms.
For a Cartesian robot, the pick and place automation of heavy loads is easy because its bearings and support frames are able to prop the entire range of motion. To better illustrate the point, imagine a load of 110 pounds. The weight is well within the payload range of all the three robots; however, 110 pounds is at the upper end of the SCARA’s capacity; it will, therefore, take more controls and extra parts to handle the resulting torque.
But with a Cartesian robot, the support system enables it to effortlessly handle the same load without the need for additional help or components, making it the ideal pick and place industrial robot.
Orientation

Source: Pinterest
Orientation is another area that differentiates the robots from one another. When it comes to orientation, there are two main things that stand out.
How the robot parts move.
How the robot is mounted.
The goal here is to align the robot’s footprint to its working area. For example, if a Six-Axis robot or a SCARA robot is causing massive obstruction during working, then using such robots is not ideal in that situation. However, if the movement requires the least number of axes, then a Cartesian robot would be a better bet as it can be mounted overhead, leaving enough room below for other things.
At the same time, if the task in question involves complex handling or it is work that needs more axes, then a SCARA robot that can occupy the least amount of space but still use the most number of axes would be the better option. Orientation depends largely on the space and the nature of the task at hand.
Speed and Travel

Source: Pinterest
A high-speed robot arm is a major factor when it comes to differentiating industrial robots. There are some tasks that require high speeds and others that require precision to take precedence. A robot’s speed is not just limited to its handling of materials; it is also based on the distance it travels around the space provided.
Cartesian robots can accelerate at about 5m/sec, sometimes even more, if they are smaller and nimble. SCARA and Six-Axis robots are much slower compared to that. Another feature that makes Cartesian robots superior in this regard is the fact that they can be modified to cover more distance at faster speeds if they are paired up by the right bet, ball screw actuator, or a linear motor.
Cartesian robots are anchored to a flexible overhead rail, which can be extended to great distances, making them good industrial robot types. SCARA and Six-Axis robots, on the other hand, are fixed on pedestals that rarely move.
Positional Accuracy

As far as accuracy is concerned, SCARA and Six-Axis robots are a little more accurate than their Cartesian counterparts. For a Cartesian robot to clock the same level of accuracy, they will need to be fitted with extra components and parts that enhance that feature. The said parts include ball-screw actuators and precision machined ball-rail tables.
At the same time, there are instances where SCARA and Six-Axis robots are unable to maintain their accuracy due to robotic arm deflection. In instances like these, Cartesian robotic arms with high-precision linear bearings that minimize deflection that allows the end effector to be positioned more accurately are a better option. Ultimately, the speeds of each of these robots depend on the task they are handling.
The Environment

Source: Pinterest
The working environment and the hazards present are another two factors that can be used to set these three robots apart from each other. For SCARA and 6-Axis robots, their pedestals are compact, which allows them to occupy the least amount of space; however, this fixed nature can render them obsolete in an environment where the robot’s support frame can be installed overhead as in the case of a Cartesian robot.
Dust and dirt also affect the type of robot that people choose to go with. SCARA and Six-Axis robots are more prone to being affected by dust than Cartesian robots, which use more movements. Robots can be covered to minimize corrosion from dust and first in their moving parts, but these will ultimately hinder efficient movement.
Top Industrial Robot Manufacturers

Having looked at the differences that set apart SCARA, a Six-Axis robot arm, and Cartesian robots, it is also vital to know the manufacturers who are behind their creations. The following are some of the top industrial robotic arm manufacturers in the world.
EPSON

Source: Epson
EPSON is a robot manufacturer that has been in the business for over 35 years. They are best known for the top of the range Six-Axis robots that are equipped with the most advanced robot tech on top of their ability to handle huge payloads. Their Six-Axis robots have a payload of about 10 pounds and a robotic arm reach of between 450mm to 1,480mm. The EPSON RC+ software that is used in all of their robots has Vision and Force Guidance features for better functionalities.
EVS

EVS is a world leader when it comes to the creation of industrial robots. As a leading SCARA robot manufacturer, among their stand out products, their SCARA models are among the most advanced in the industry. Their catalog features two advanced SCARA robots, a smaller one with a 5-pound payload and a 400mm arm reach, and a much larger one with an 8-pound payload and a 600mm arm reach.
Most EVS robotic arms are in high demand across the globe and are widely used in the automotive and aerospace industries due to their high speeds, advanced technologies, and ingenious designs.
Yamaha Motor Corporation

Source: yamaha-motor.com
Yamaha Motor Corporation is the world’s leading manufacturer of Cartesian robots. Mostly known for its superbikes that are used in many international races, Yamaha Corporation is also a prominent manufacturer and supplier of industrial robots with a particular focus on Cartesian ones. Their catalog features cartesian robots of all types. The company also manufactures SCARA robots and single-axis ones.
Conclusion
As the wheels of technology continue to turn, more refined versions of industrial robots continue to be released every year. With each new model, the weaknesses that plagued the previous versions get smaller and smaller. It is only a matter of time before every aspect of human life will be entirely dependent on industrial robots. Whether that will be a good or a bad thing is yet to be determined.
